For What Purpose Do Bacteria Utilize Restriction Enzymes. Restriction enzymes bind to recognition sequences in dna, usually 4 to 8. Web bacteria use restriction enzymes to protect themselves from a dangerous virus called a bacteriophage, which translates to bacteria eater in literal terms.
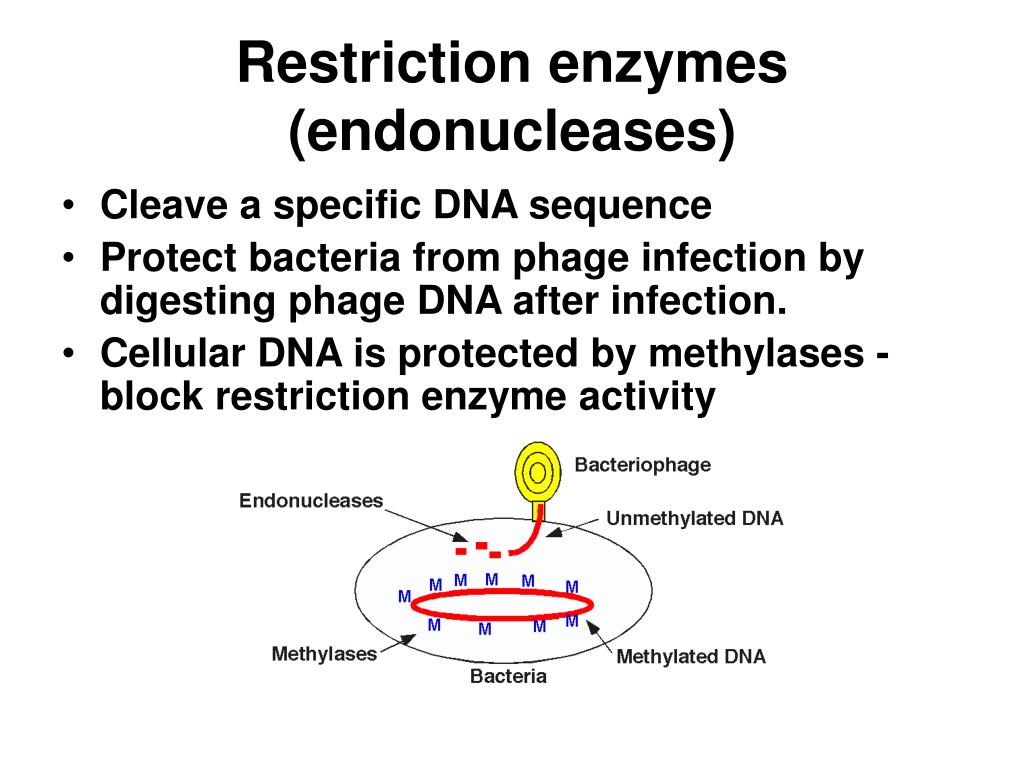
Web bacteria prevent eating away their own dna by masking the restriction sites with methyl groups ( ch 3 ). Nature education 1 (1) :38 restriction enzymes are one. In bacteria, restriction enzymes cleave foreign dna, thus eliminating infecting organisms.
However, Quantitative Digestion Can Sometimes Only Be Achieved After Extended Incubation (I.e.
Because they cut within the. Restriction enzymes bind to recognition sequences in dna, usually 4 to 8. They recognize and cleave at the restriction sites of the bacteriophage and destroy its dna.
These Viruses Attack Bacteria By.
Well, restriction enzymes occur naturally in bacteria and bacteria use them themselves to break up dna, foreign dna, that infects bacterial cells. Web bacteria use restriction enzymes to protect themselves from a dangerous virus called a bacteriophage, which translates to bacteria eater in literal terms. Nature education 1 (1) :38 restriction enzymes are one.
Web Restriction Enzyme Function In The Natural World Is To Defend Bacteria Against Specific Viruses Called Bacteriophages.
Methylation of dna is a common way to modify dna. Web tufts university & harvard. The main components include restriction enzyme (r), which cuts specific.
Web The Restriction Enzymes Protect The Live Bacteria From Bacteriophages.
Web restriction enzymes (also called restriction endonucleases) are proteins made by many bacterial species, to defend against viral infections. Just like other organisms, bacteria can be. Web in fact, it is quite common to use two different enzymes and this allows us to do directional cloning — i.e.
Web A Restriction Enzyme, Restriction Endonuclease, Rease, Enase Or Restrictase Is An Enzyme That Cleaves Dna Into Fragments At Or Near Specific Recognition Sites Within.
In bacteria, restriction enzymes cleave foreign dna, thus eliminating infecting organisms. Web bacteria prevent eating away their own dna by masking the restriction sites with methyl groups ( ch 3 ). Web forty years ago, the scientists whose pioneering work had explored the activity and sequence specificity of these enzymes, contributing to the definition of their enormous.